Simple Explanation Of Crypto Gas Fees For Students (2025 Guide)
What Are Crypto Gas Fees in Simple Words?
If you are trying to learn crypto gas fees, here’s a simple explanation of crypto gas fees for students:
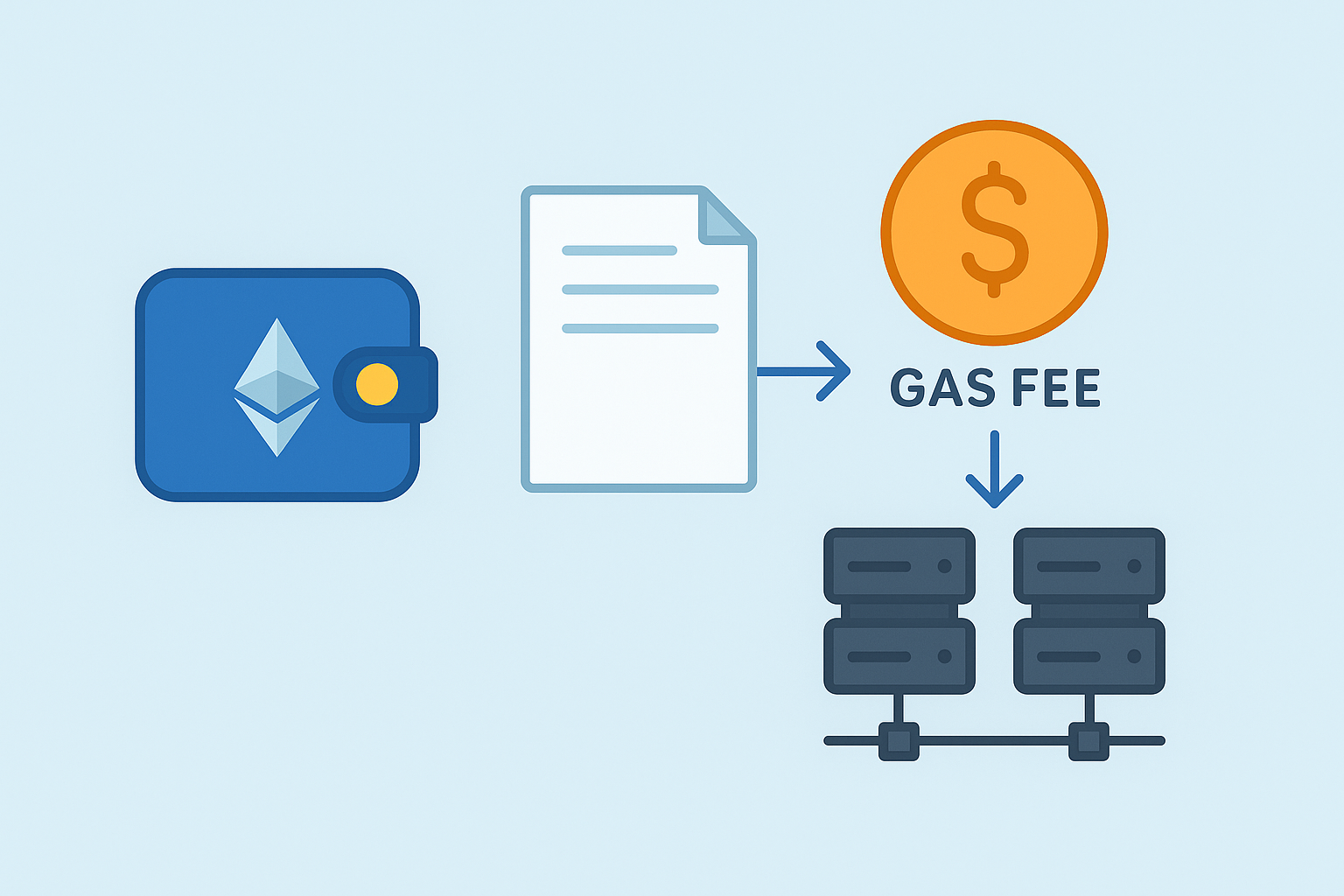
Gas fees are the cost you pay to use a blockchain network.
When you send cryptocurrency or interact with a blockchain app, computers called miners (or validators) help process and confirm your transaction. These computers use energy and computing power, so they charge a small fee—this is called a gas fee.
🔑 Think of it Like This:
Imagine sending a package through a delivery service.
- The delivery trucks = Blockchain computers (miners)
- The delivery fee = Gas fee
- The package = Your crypto transaction
Without paying a delivery fee, your package (transaction) wouldn’t get delivered. Similarly, without paying gas fees, your crypto actions won’t be completed.
⚙️ Where Are Gas Fees Paid?
Gas fees are paid on many blockchains.
Here are some examples:
- Ethereum: Gas fees are paid in ETH.
- Binance Smart Chain: Paid in BNB.
- Polygon: Paid in MATIC.
✅ Why Do Gas Fees Matter for Students?
If you’re learning crypto, understanding gas fees helps you:
- Avoid overspending on transactions.
- Choose cheaper blockchains like Polygon when practicing.
- Know when the network is too busy or too expensive.
Bottom Line:
To put it simply, crypto gas fees are the small costs you pay to use a blockchain network.
Learning this early helps you use crypto smartly—and avoid mistakes with your money later.
Why Do Gas Fees Change?
When learning about crypto, it’s important to understand why gas fees change over time.
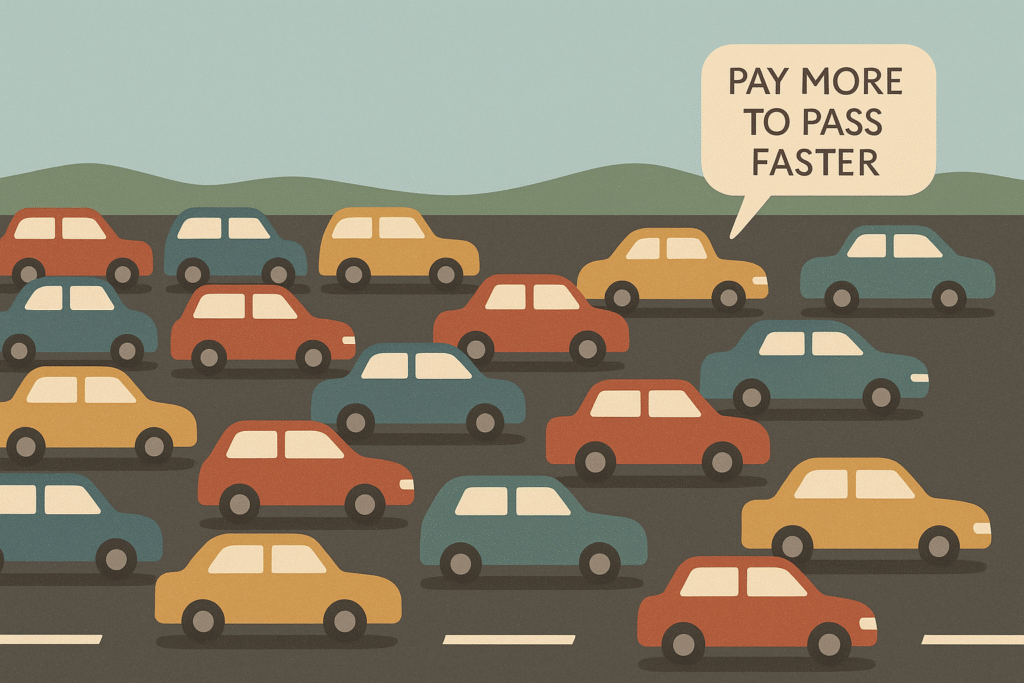
This simple explanation of crypto gas fees for students will help you see that gas fees work like traffic on a highway. When more people use the blockchain at the same time, the network gets busy, and gas fees go up.
✅ Main Reasons Gas Fees Go Up or Down:
🔹 1. Network Congestion (Busy Times)
- If a lot of people are sending crypto or using dApps at once, the network becomes crowded.
- Everyone is competing to get their transaction processed quickly.
- The blockchain miners/validators prioritize higher-paying transactions, causing fees to rise.
🔹 2. Type of Transaction
- Simple transactions (like sending ETH) use less gas.
- Complex actions (like minting an NFT or swapping on a DeFi app) use more gas.
🔹 3. Blockchain Type
- Ethereum tends to have higher gas fees than blockchains like Binance Smart Chain or Polygon.
- This is because Ethereum is more popular but has limited transaction space.
🔹 4. Time of Day
- Gas fees often change throughout the day.
Example:- Peak hours (daytime in the U.S.): Higher fees
- Late-night hours or weekends: Lower fees
🔍 Example in Simple Words:
If 1,000 people try to use the blockchain at the same time, the network gets crowded—just like a traffic jam. To get through faster, some people pay extra (higher gas fees).
Where Are Gas Fees Used in Crypto?
If you’re wondering where gas fees come into play in crypto, here’s a simple explanation of crypto gas fees for students:
Anytime you use the blockchain, you are asking computers to process your transaction. Those computers (called miners or validators) use energy and resources. To reward them, you pay gas fees. This applies to more than just sending cryptocurrency.
✅ Common Places Where Gas Fees Are Charged
🔹 1. Sending Cryptocurrency
Every time you send ETH, BNB, or MATIC from one wallet to another, you pay a small gas fee. This is the most basic blockchain transaction.
🔹 2. Swapping Tokens on Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
When you swap one token for another on platforms like Uniswap, PancakeSwap, or QuickSwap, you pay gas fees to process that trade.
🔹 3. Minting or Buying NFTs
If you mint (create) or buy an NFT on platforms like OpenSea or Blur, you pay gas fees to complete the transaction.
🔹 4. Deploying Smart Contracts
Developers pay gas fees when they upload (deploy) a new smart contract to a blockchain.
🔹 5. Using dApps (Decentralized Apps)
Anytime you use a blockchain-based app (lending, staking, playing games), actions that interact with the blockchain require gas fees.
📝 Quick Example:
If you’re swapping tokens on Uniswap:
➡️ Gas fees pay for finding the best trade path, updating the blockchain, and confirming your transaction.
How Can Students Practice Without Paying Real Gas Fees?
The best way for students to learn about crypto without spending money is to use testnets. This is part of the simple explanation of crypto gas fees for students—testnets allow you to practice everything safely and for free.
Testnets are fake blockchain networks where you use free, fake tokens instead of real money. Even though you still pay gas fees on a testnet, those fees are paid with free testnet tokens—not your own crypto.
✅ Steps for Students to Practice on a Testnet
🔹 1. Install a Crypto Wallet
Download MetaMask, Trust Wallet, or another beginner-friendly crypto wallet.
🔹 2. Switch to a Testnet Network
In your wallet, change the network from the mainnet to a testnet.
Examples of popular testnets:
- Ethereum Goerli Testnet
- Binance Smart Chain Testnet
- Polygon Mumbai Testnet
🔹 3. Get Free Testnet Tokens (Faucets)
Visit faucet websites to get free tokens.
Examples:
- Goerli Faucet → goerlifaucet.com
- Binance Testnet Faucet → testnet.binance.org/faucet-smart
- Polygon Faucet → faucet.polygon.technology
Paste your wallet address to claim free tokens. No payment is needed.
🔹 4. Practice Transactions Safely
- Send and receive fake crypto on the testnet.
- Swap tokens using testnet versions of DEXs.
- Try deploying a smart contract.
🛡️ Why This Helps Students:
- No real money involved.
- Safe space to learn about gas fees.
- Practice before using the main blockchain (mainnet).
How to Save on Gas Fees (Student Budget Tips)
For students learning crypto, saving on gas fees is important because you don’t want to waste your limited funds. This simple explanation of crypto gas fees for students gives you practical tips to spend less while learning.
Gas fees aren’t always fixed. If you time your transactions and use the right tools, you can reduce your costs—making your learning experience cheaper and smarter.
✅ Smart Ways to Save on Gas Fees
🔹 1. Use Blockchains With Lower Fees
- Ethereum gas fees are expensive.
- Try cheaper networks like:
- Polygon (MATIC)
- Binance Smart Chain (BNB)
- Avalanche (AVAX)
🔹 2. Avoid Busy Times (Network Congestion)
Gas fees are highest when many people use the network.
To save money:
- Use the network at nighttime (US time zones).
- Make transactions on weekends when traffic is lower.
🔹 3. Combine Small Transactions
Instead of sending crypto multiple times, batch your actions into one bigger transaction.
This way, you pay the gas fee once, not several times.
🔹 4. Use Layer 2 Networks
On Ethereum, try using Layer 2 solutions like:
- Arbitrum
- Optimism
- zkSync
These reduce gas fees while still using Ethereum’s security.
🔹 5. Practice on Testnets First
Before spending real money, learn how gas fees work on testnets (practice blockchains). This helps you avoid mistakes that could cost real crypto.
📉 Example:
Sending ETH on Ethereum mainnet = $5 to $20 in gas fees.
Sending the same token on Polygon Mumbai Testnet = Free (using fake tokens).
Conclusion: Understand Gas Fees to Be a Smarter Crypto User
Gas fees may sound confusing at first, but with a simple explanation of crypto gas fees for students, you now know they are just the cost of using a blockchain network.
The smart way to learn crypto as a student is to:
- ✅ Start practicing on testnets where you won’t lose real money.
- ✅ Understand what causes gas fees to rise and fall.
- ✅ Choose cheaper blockchains like Polygon or Binance Smart Chain to save costs.
- ✅ Time your transactions during low network traffic.
By learning these basics, you’ll avoid mistakes, protect your money, and grow your blockchain skills safely.
🎯 Final Tip:
Always practice first and spend carefully—your future in crypto starts with safe, smart learning.
https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/gas/
https://www.coinbase.com/learn/crypto-basics/what-is-a-gas-fee
https://academy.binance.com/en/articles/understanding-bnb-smart-chain-transaction-fees
https://wiki.polygon.technology/docs/faq/gas-fees/
https://docs.alchemy.com/docs/ethereum-transaction-gas-fees
https://etherscan.io/gastracker
https://faucet.polygon.technology/
https://goerlifaucet.com/
https://testnet.binance.org/faucet-smart






